For thousands of years, farmers milked their cows by hand, a labour-intensive task that required skill, patience, and a deep understanding of the animals.
The advent of the Industrial Revolution brought about the first significant shift in this practice. In the late 19th century, cow milking machines were introduced, heralding a new era in dairy farming.
By the early 20th century, the milking machine had evolved into a more refined apparatus featuring vacuum pumps and pulsators that mimicked the natural rhythm of calf suckling.
With the help of these machines, a single farmer can milk hundreds of cows in a day. This efficiency boost is crucial in meeting the global demand for milk and dairy products, which continues to grow as the world’s population expands and countries develop.
The precision and consistency offered by mechanical milking ensure a higher standard of milk quality and safety. Automated systems monitor various factors such as milk flow and udder health, ensuring that each cow is milked optimally. This system not only improves the quality of the milk but also enhances the welfare of the cows, reducing the risk of udder infections and other health issues.
Photo by: Wolfgang-Ehrecke
What is a Cow Milking Machine?
It is an automated system that replicates the action of a calf suckling, making the process faster, more consistent, and less labour-intensive than manual milking. The core principle behind these machines is to draw milk from the cow’s udder gently but effectively using a combination of pulsation and suction.
Components of a Cow Milking Machine
The typical cow milking machine consists of several key components:
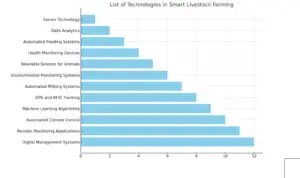
- Teat Cups: These components are directly attached to the cow’s teats. Each teat cup has a rubber or silicone liner inside a metal or plastic shell. The liner gently compresses and releases the teat, simulating the action of a calf’s mouth.
- Vacuum Pump: This creates a vacuum that helps draw milk out. The vacuum also holds the teat cups in place. The vacuum level must be carefully controlled for the comfort and health of the cow.
- Milk Container: This is where the milk is collected after being drawn from the udder. This container could be a bucket, a large central tank, or a direct pipeline to a cooling and storage facility in different systems.
- Pulsator: This device rhythmically controls the air pressure inside the teat cups, alternating between vacuum and atmospheric pressure. This action massages the teat, ensuring milk is extracted efficiently without causing discomfort or harm to the cow.
- Milk Tubes: These tubes transport the milk from the teat cups to the container. They are designed to be easily cleaned and sanitized.
- Control Panel/System: In modern milking machines, especially automated ones, there is a control system that monitors and adjusts the milking process, ensuring optimal efficiency and cow udder health.

Types of Milking Systems
Milking machines come in various types to suit different scales and styles of dairy farming:
- Bucket System: The simplest form of a milking machine, where milk is drawn into a portable bucket. Ideal for small farms or minimal dairy operations, this system is easy to use and clean but requires manual milk handling after extraction.
- Pipeline System: In this setup, milk is drawn and transported through sanitary pipes to a central cooling and storage tank. This system is more efficient and hygienic than bucket systems and is suitable for medium- to large-sized farms.
- Rotary Parlours: Designed for large, industrial dairy farms, rotary parlours are sophisticated systems where cows stand on a slowly rotating platform during milking. Each cow steps onto the platform, gets milked by an automated system, and steps off once milking is completed.
- The Robotic Milking Machines: A robotic milking machine represents a significant advancement in dairy farming technology. It automates the milking process, allowing cows to be milked without direct human involvement.
Key feature of the robotic milking machine
- Automation: The entire milking process is automated. When ready, cows enter the milking area, often lured by a feed incentive. Sensors identify the cow, and robotic arms clean the udder and attach teat cups.
- Laser and Sensor Technology: These machines use sophisticated laser-guided systems and sensors to locate the teats, correctly attach the milking apparatus, and monitor the process. This technology ensures precision and reduces the risk of injury or discomfort to the cow.
- Individualized Care: The system records data for each cow, like milk yield, milking frequency, and udder health. It also analyzes the milk to identify infection. Everything allows for personalized care and early detection of potential health issues.
- Voluntary Milking: Cows can decide when to be milked, which often leads to increased frequency in milking and, consequently, higher milk yield. This system respects the natural behaviour and preferences of the cows, contributing to their welfare.
- Reduced Labor: Since the process is automated, the need for manual labour is significantly reduced. Farmers can focus on other aspects of farm management while the robotic system handles the milking.
- Consistency and Hygiene: Robotic milking machines maintain high standards of consistency and hygiene, which positively impacts milk quality. They ensure that the milking process is as hygienic and gentle as possible.
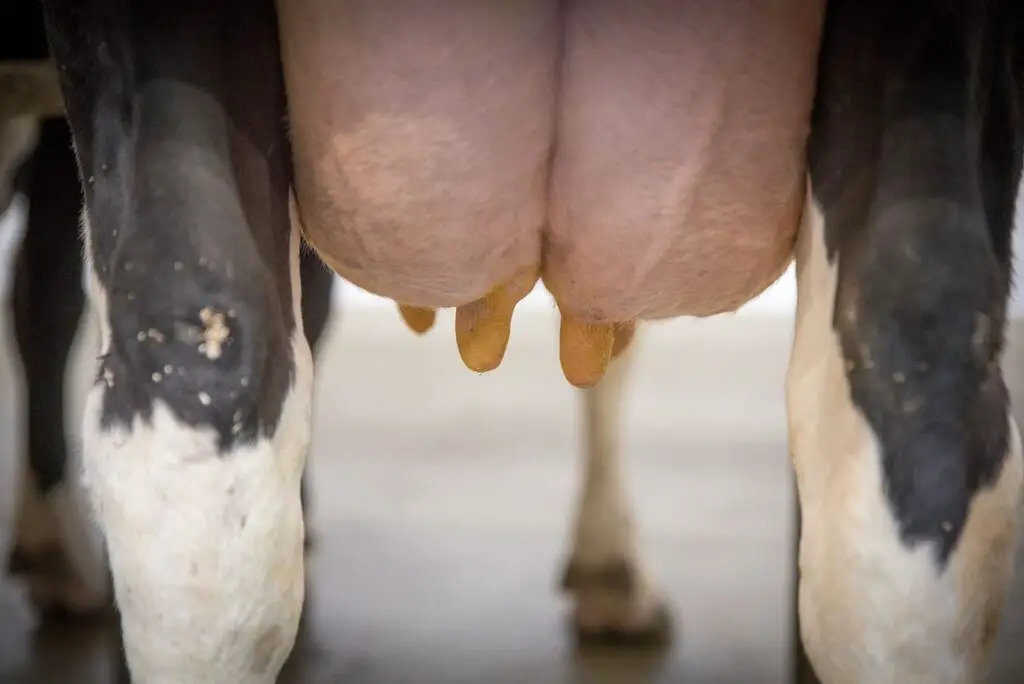
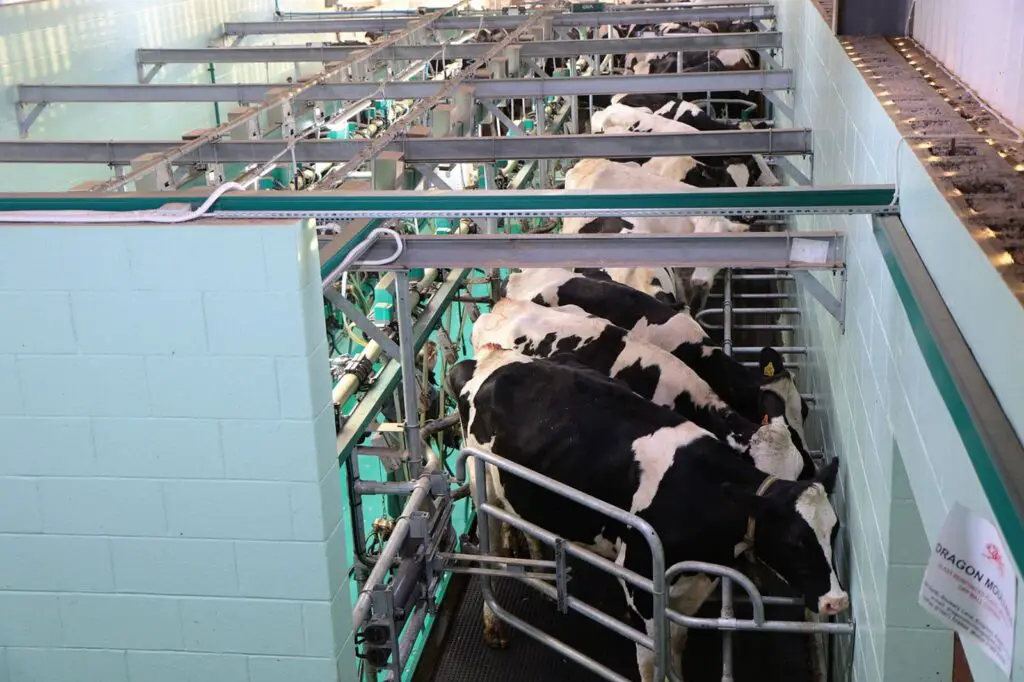
Step-by-Step Explanation of the Milking Process
- Preparation: The cow’s udder is cleaned and sanitized. This part is crucial for maintaining hygiene and preventing the spread of bacteria into the milk and onto the cow’s skin.
- Attachment of Teat Cups: The teat cups, each with a liner, are attached to the cow’s teats. A farmer does this in manual systems, while robotic systems use sensors and automated arms.
- Creating Vacuum: Once the teat cups are in place, the milking machine creates a vacuum around the teats. This vacuum is crucial as it simulates the sucking action of a calf.
- Milking: The vacuum draws milk from the teats and into the machine. The milk is transported through tubes into a storage bucket or directly to a cooling and storage system.
- Pulsation: This is where the pulsator comes in. It intermittently breaks the vacuum, allowing the teat to refill with milk. The pulsation is gentle and rhythmic, preventing discomfort or damage to the teat tissue.
- Completion: Once milking is complete, the machine detects the decrease in milk flow and automatically removes the teat cups. The cow is then released.
Benefits of Using Milking Machines
The advent of milking machines has brought many benefits to the dairy industry, transforming how dairy farms operate. These benefits range from operational efficiencies to improved animal welfare.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Milking machines significantly speed up the milking process, allowing more cows to be milked in less time. This increase in efficiency translates to higher productivity, enabling farmers to manage larger herds and produce more milk without a corresponding increase in labour.
- Improved Milk Quality and Consistency: Mechanical milking ensures that the process is uniform and controlled, which helps maintain the quality and consistency of the milk. These machines are designed to minimize milk contamination, leading to a safer and higher-quality product.
- Enhanced Animal Welfare: Modern milking machines are designed to be gentler and less stressful for cows than manual milking. They provide consistent suction and pulsation, reducing discomfort and the risk of injuries to the udder or mastitis infections. Automated systems allow cows to be milked on their schedule, which aligns more closely with their natural behaviours.
- Labour Reduction and Economic Benefits: Milking machines reduce the need for manual labour, which can be physically demanding and time-consuming. This labour reduction can translate into significant economic savings for farmers, allowing them to allocate resources and workforce to other aspects of farm management.
Challenges and Considerations
While milking machines offer numerous advantages, there are also challenges and considerations that farmers must address:
- Maintenance and Cleanliness of the Machines: Regular maintenance and thorough cleaning of milking machines are essential to ensure their proper functioning and to maintain milk hygiene. Neglecting maintenance can lead to equipment breakdowns and contamination of milk.
- Ensuring Animal Health and Avoiding Mastitis: While milking machines generally improve animal welfare, improper use or malfunctioning equipment can increase the risk of mastitis, a painful infection of the udder. Monitoring the machines and the cows’ health is critical to prevent such issues.
- The Initial Cost and Learning Curve for Farmers: The upfront cost of purchasing and installing milking machines can be significant, especially for small-scale farmers. A learning curve is also associated with operating and maintaining these machines effectively.
- Adapting to Different Sizes and Breeds of Cows: Milking machines must be adaptable to accommodate different sizes and breeds of cows, each with unique physical characteristics. Adjustments and calibrations are often necessary to ensure that the machine works effectively for all cows in a herd.
The Future of Cow Milking Machines
The future of these machines is intertwined with emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and machine learning, which are set to redefine the standards of efficiency, sustainability, and animal welfare.
1. Technological Advancements: IoT, AI, and Machine Learning
- Internet of Things (IoT): The integration of IoT in milking machines will allow for real-time monitoring and data collection, offering insights into the health and productivity of each cow. Sensors will track various parameters such as milk yield, temperature, and udder health, transmitting this data for analysis and action.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI will play a significant role in analyzing the vast amounts of data IoT devices collect. Machine learning algorithms can predict and detect issues like potential udder infections or nutritional deficiencies, enabling preemptive measures. This technology can also optimize milking schedules and routines based on individual cow behaviour and needs, ensuring maximum efficiency.
- Automation and Robotics: The advancement in robotics will further automate the milking process, reducing the need for human intervention and ensuring precision and consistency. Robots with advanced sensors can adapt to different cow sizes and breeds, providing a customized milking experience.
2. Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Practices in Milking
- Energy Efficiency: Future milking machines will be designed with a greater emphasis on energy efficiency, reducing the carbon footprint of dairy operations. Solar-powered systems and other renewable energy sources could be integrated into milking machines.
- Water Conservation: Water is a crucial resource in dairy farming, and future milking technologies will focus on reducing water usage with innovations in cleaning and sanitizing systems that use less water without compromising hygiene.
3. Impact on the Global Dairy Industry
- Increased Global Milk Production: The continued evolution of milking machines will enable dairy farms to become more productive, meeting the growing global demand for milk and dairy products.
- Economic Viability for Small-Scale Farmers: Technological advancements might become more accessible and cost-effective, allowing small-scale farmers to benefit from these innovations, thereby improving their competitiveness and profitability.
- Enhanced Animal Welfare Standards: With technology focusing on animal health and comfort, the future of dairy farming will likely see higher animal welfare standards, which are increasingly important to consumers.
Conclusion
The evolution of cow milking machines from manual to mechanical and now to advanced automated systems encapsulates the remarkable innovation journey in dairy farming.
From the initial mechanical devices of the late 19th century to today’s sophisticated, AI-powered robotic systems, these machines have enhanced efficiency and revolutionized how we approach dairy farming.
Milking machines have become indispensable in modern dairy operations by increasing productivity, ensuring consistent milk quality, promoting animal welfare, and reducing labour.
As technology evolves, so will these machines’ capabilities and benefits. They are set to play an essential role in meeting the growing global demand for dairy while upholding environmental responsibility and enhancing the welfare of the cows that are central to this industry.
Share your thoughts, experiences, and expectations for the future of cow milking machines in the comments below.