Recycling transforms waste into a new material using processes that allow us to reuse the raw material presented in the disposed item. The modern form of recycling started in the 1960s and has evolved since then, with multiple new business models adopting a more “circular” practice.
Modern recycling processes vary between nations depending on their demand and capacity. Urban recycling focuses on extracting and processing glass, paper, aluminium cans, and plastics. The effectiveness of recycling in urban areas is highly dependent on proper disposal practices, which highlights why recycling is important.
Recycling is essential for conserving natural resources and reducing environmental footprint. It lowers energy consumption, diminishes greenhouse gas emissions, and minimizes waste in landfills, thereby protecting ecosystems and biodiversity.
Economically, recycling supports job creation, contributing to wages, sales, and tax revenues, fostering sustainable growth. On a community level, it enhances social cohesion and provides educational and fundraising opportunities.
The process involves collection, processing, and manufacturing, requiring modern infrastructure and an informed public.
Main Takeaways
Recycling transforms waste into reusable raw materials, conserving resources and reducing environmental impact.
- Environmental Benefits
- Saves energy (e.g., recycling steel saves up to 74% of energy compared to raw extraction).
- Reduces habitat destruction, pollution, and biodiversity loss.
- Helps prevent ocean pollution and mitigates climate-related landfill challenges.
- Economic Benefits
- Generates jobs: Recycling 10,000 tons creates 36 jobs versus one from incineration.
- Contributes significantly to economies, with $236 billion in sales and $37 billion in payroll in the U.S. (2020).
- Fosters growth in industries like second-hand markets and sustainable manufacturing.
- Social Benefits
- Strengthens community bonds through initiatives like thrift stores and upcycling.
- Encourages sustainable consumer practices, especially among eco-conscious younger generations.
- Challenges in Recycling
- Complexity in processing hybrid materials and electronics (e.g., WEEE).
- The high costs of material separation and the need for more demand for recycled products hinder economic viability.
- Consumer attitudes and inadequate awareness often perpetuate a throwaway culture.
- Solutions and Future Outlook
- Integrating sustainability into product design (eco-design and life cycle assessment).
- Advancing recycling technologies for complex materials.
- Strengthening policies (e.g., tax incentives, stricter regulations) to support recycling systems.
- Promoting consumer education to drive demand for sustainable products.
- Developing closed-loop systems for a circular economy.
What Are the Environmental Benefits of Recycling?
Recycling is more than just a practical solution to waste—it’s a lifeline for the environment, preserving the planet’s resources. Whenever we toss a plastic bottle into a recycling bin or repurpose old paper, we are part of a process that reduces the strain on Earth’s forests, waters, and air.
Effective Way to Save Energy and Reduce CO2 Emissions.
One example of energy savings through recycling is steel, which can save up to 74% of energy compared to extracting it from nature.
Energy savings from recycling result from the reduced need for mining and transporting and the intensive use of high-temperature furnaces that produce aluminium, steel, and other materials.
Incineration is a common practice that seeks to reduce the volume of waste produced by burning trash at high temperatures. Recycling reduces incineration by adding value to the disposed material.
While incineration can be used to create energy in a process called waste-to-energy (adopted in Japan, northern Europe, and South Korea), the energy saved by recycling certain products is still higher. Once inserted into a circular practice, the recycled component avoids additional raw material extraction from nature, adding more value to the product.
Recycling Also Plays a Crucial Role in Wildlife Conservation.
Recycling reduces habitat destruction and biodiversity threats by decreasing the need for raw material extraction. Mining and logging activities can lead to significant habitat loss for many species, increasing their risk of extinction.
Recycling helps prevent waste, especially harmful substances like plastic, from reaching natural habitats, where they can harm wildlife.
Recycling helps to keep the oceans clean. Recent estimates predict that nearly 10 million tons of plastic are washed into the ocean yearly. Most of this content is associated with inadequate disposal and missed recycling opportunities. Recycling reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills. As landfills represent a serious challenge for urban areas, keeping the volume of waste added to these sites low is important to support natural preservation. With climate change and rising sea levels, certain urban areas face the challenge of improving landfill management due to the risk of flooding and contaminant dissemination.
Recycling Supports Preservation of Natural Ecosystems
Reducing the extraction intensity needed to supply our raw material needs reduces our environmental footprint by lowering contaminant emissions, pollution, and ecological damage.
On average, 1 ton of recycled paper uses 23,000 litres less water than is required to obtain the same amount of paper from nature. Therefore, avoiding water extraction keeps water in nature, supporting local ecosystems.
Recycling also reduces greenhouse gas emissions due to the energy savings it brings. As mentioned, producing raw materials can be very energy-demanding, with items such as cement, steel, and aluminium accounting for over 15% of global energy consumption. Recycling directly reduces the estimated GHG emissions per product by reducing demand in these industries.

What Are the Economic Benefits of Recycling?
Many often overlook the substantial economic benefits associated with recycling. In 2020, recycling and reuse activities accounted for 681,000 jobs in the United States, generating an impressive $37.8 billion in wages.
While incinerating 10,000 tons of waste creates merely one job, recycling the same amount of materials creates 36 jobs.
The recycling industry contributes considerably to national and local economies. It generates $236 billion in sales and $37 billion in payroll.
Additionally, the industry contributes $5.5 billion in tax revenues, indicating its positive impact on public finances.
A recent Greenpeace study shows that recycling can generate up to 39 times more job positions than incineration processes. Recent analysis in the UK shows that currently, 144,185 people are employed in the waste sector, with estimates increasing this number to 472,000 by 2035 if investments in the green industry remain.
What Are The Social Benefits of Recycling?
Recycling and repurposing can be an excellent social glue, connecting communities and strangers. Recycling products can be reached through upcycling, which consists of giving your old product a new use (or owner). The best example of a successful repurpose practice is thrift shops, which focus on resale of used items for a reduced cost. Between 2016 and 2021, the clothing resale market has grown by 109.4%, with multinational brands adopting multiple circular practices.
Second-hand local stores are increasing their use of recycled items under the concept of vintage. Gen Z shoppers are particularly aware of the impacts of their consumerism and adopt the thrift shopping practice as an exciting alternative to online shopping. Estimates forecast that the second-hand market will reach $77 billion a year, supporting the growth of this eco-friendly alternative.
Recycling materials is good for the environment because it reduces the need for new raw materials. Similarly, repurposing clothing, furniture, garments, etc., reduces our pressure on nature by reducing our demand in the industry. For example, buying second-hand jeans saves up to 1800 gallons of water needed to grow the cotton required for production.

Is Recycling an Answer to the Plastic Waste Problem?
Plastic pollution is a worldwide problem, especially due to the low level of recycling. As plastic production is typically low-cost, plastic has been used and disposed of without control. Due to its physical properties, plastic is not easily degraded, requiring an industrial recycling process. Overall, plastic is sorted, crushed, melted, and reshaped into a new product, reaching final materials with the same flexibility and resistance as the original content.
The physical stability of plastic makes it a very suitable material for recycling. Unfortunately, the same properties render it almost impossible to degrade naturally, being shredded into small pellets that migrate through our food chain. The small plastic pellets are called microplastic and have recently been identified inside the human body. Despite having no proven direct correlation with diseases for humans, microplastics have become a growing cause of fish deaths as they are pointed to starve more frequently and change their eating patterns to higher-risk behaviours.
How to Recycle
The first step to improving your recycling is understanding how to recycle within your local facility. Recycling practices change according to the recycling unit’s equipment and processes, and different requirements are passed out to household clients.
The most important thing to remember when understanding how to recycle is to separate all recyclable content and avoid contamination from other materials, such as mixing paper, glass, and non-recyclable items.
One of the main challenges with waste sorting is the presence of batteries in the sorted content. Batteries cause nearly 700 fires yearly in waste processing centres and emit toxic chemicals that can cause contamination at recycling units and landfills.
Another problem is the accumulation of residue in recycled content. Oils, fats, grease, and creams found as residue in recyclable content make it challenging for companies to operate adequately, pushing for more intense re-sorting and cleaning of the content.
Last, it is important to understand that recycling practices depend on local suppliers and change within countries and cities. Some countries have additional fines for those who fail to recycle adequately and financial compensation for those who abide by the rule. Overall, global trends are shifting to improving recycling practices and ensuring that cities are more energy efficient, less pollutant, and greener.
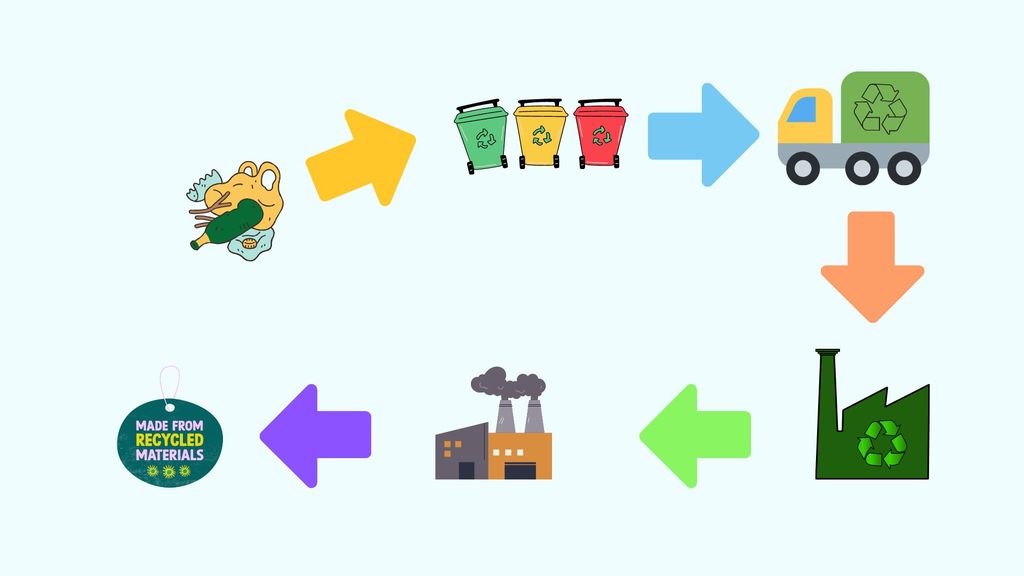
The Main Process of Recycling Consists of the Following Steps:
- Sorting: separating the waste per product and according to recommendations. Note that sorting practices vary among cities and even urban areas depending on how the local recycling industry is designed.
- Disposing: Proper waste disposal into bins and bags and collecting points is extremely important. Clear-marked bins, constant awareness campaigns, and a clear description of sorting practices are key in this step.
- Recycling: Individual process units are designed for recycling glass, paper, aluminium, plastics, etc. Recycling treatment involves chemical and physical steps, with heating units, melting points, and chemical baths as part of the industrial process.
- Commercialization: The recycled content is then sold to other businesses that use it as a raw component in their industrial processes.
- New end material: The recycled component is embedded in new products and reaches the market. At this stage, companies are motivated to promote using recycled components in their materials, which we can identify in clothing, household materials, furniture, etc.

The Challenges of Recycling
Recycling faces numerous challenges rooted in economic, technical, and societal factors.
Economically, the primary drivers for recycling initiatives are cost savings, competitive advantage, and raw material prices. Yet, these same factors can act as barriers when the financial benefits are unclear or insufficient.
The complexity of modern industrial systems further complicates recycling efforts, as products today are often composed of hybrid materials and composites that are difficult to separate and recycle efficiently.
For instance, while bulk metals have established recycling systems, recovering metals from Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment —a rapidly growing waste stream—remains problematic due to the heterogeneity of components and hazardous materials, such as lead and mercury, that require careful handling.
The lack of efficient recycling processes for such complex products, coupled with mixing materials like plastics and fillers, diminishes the economic incentive for recovery, as the cost of separation often outweighs the value of the retrieved materials.
Additionally, the availability and accessibility of critical raw materials pose a vulnerability in the global supply chain, highlighting the need for improved recycling systems to prevent resource depletion.
The design phase of products also plays a crucial role; decisions made early in the product life cycle significantly influence its recyclability. However, tight scheduling and limited access to environmental data during this phase hinder the integration of sustainable design practices.
Societal attitudes contribute to the recycling challenge, as consumers frequently prioritize new technologies and brand appeal over environmental considerations, perpetuating a throwaway culture. Despite stricter regulations, such as the EU’s directives on WEEE and hazardous substances, the lack of market demand for recyclable products and insufficient awareness of life cycle impacts limit progress.
Overcoming Challenges – The Future of Recycling
Addressing recycling challenges requires a holistic approach that integrates technological innovation, policy development, and shifts in consumer and industry behaviour.
One critical solution is adopting life cycle assessment (LCA) and eco-design principles during the early stages of product development. By incorporating sustainability into product design, manufacturers can create easier products to disassemble, recycle, and repurpose, thus minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency. Developing new, specialized recycling processes for complex and hybrid materials, such as those found in Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE), is another vital step. Advanced separation technologies and automated systems can help recover valuable metals and reduce contamination, making recycling more economically viable.
Policy measures also play a significant role; governments can incentivize recycling through tax relief, subsidies for research and development, and long-term collaborations with industrial stakeholders. Furthermore, stricter regulations, like the EU’s directives on WEEE and hazardous substances, can compel manufacturers to reduce harmful materials in their products and establish effective collection and recycling schemes.
Collaboration across industries is essential to develop closed-loop systems where end-of-life products are dismantled and recycled back into the supply chain, reducing dependency on virgin resources.
Consumer education is equally important; raising awareness about the environmental impact of their purchasing decisions can shift demand towards sustainable products, driving manufacturers to prioritize recyclability.
Finally, fostering a culture of innovation that emphasizes the business potential of sustainable practices—such as reducing production costs through material efficiency and promoting energy savings in product use—can create a win-win scenario where environmental goals align with economic benefits.
Conclusions
Recycling is indispensable for conserving natural resources, protecting ecosystems, and fostering economic growth.
Reducing waste, saving energy, and curbing greenhouse gas emissions are important ways to mitigate environmental challenges such as climate change and biodiversity loss.
Economically, recycling creates jobs, drives innovation, and strengthens local economies while offering significant cost savings for businesses and communities.
Socially, it fosters community engagement, education, and sustainable consumer practices.
Despite its benefits, recycling faces challenges that require a collaborative approach—integrating technological advancements, policy reforms, sustainable design, and consumer awareness. As we embrace these solutions, we move closer to a circular economy where waste is minimized, resources are reused, and environmental and economic goals align harmoniously.



